IMPACT ON ECONOMY:
For the banking system, the rise in bad loans led to higher provisions, which wiped
away profits and necessitated more capital infusion. But fresh capital hasn’t been
forthcoming with the government on a path of fiscal consolidation and trying to
control deficits and because of these lending has slowed down to trickle. In 2016-2017,
banks share in the flow of funds to the commercial sector dipped to 38per cent,
according to RBI’s financial stability report. This has led to reduced investments,
reduced production, unemployment, economic slowdown and finally decreasing economic
growth rate.
How to fast track resolution bad loans?
First , RBI in june had directed the banks to take the 12 largest loan defaulters,
accounting for one-fourth of the industry’s bad loans, to NCLT.
Second it prepared another list of 26 defaulters and decided that before initiating
bankruptcy proceedings, the banks should recognize the bad assets and they should
be resolved through any of the RBI’s existing bad loan resolution schemes like S4A
or SDR and only those cases which are not resolved this way should be taken to the
NCLT under the bankruptcy code. Example –the NCLT decided to dismiss the board of
unitech ltd, a leading real estate company, and directing ministry of corporate
affairs to nominate 10 directors is a good step to resolve the bad loans problem.
CENTRAL GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES:
• Banks Recapitalization • The financial resolution and deposit insurance bill,2017
• Panel to oversee PSU banks mergers
• Banks Board Bureau
• Indradhanush plan
• Merger of SBI associates with State bank of India
• Merger of Bharatiya mahila bank with SBI
• NPA ordinance
• Gyan Sangam meetings
• Passage of Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code(IBC)
• Security interest and recovery of debts laws and miscellaneous provisions (amendment)act,2016
• The payments and settlement systems(amendment)act,2015
• RBI advised all PSBs to appoint internal ombudsman
BANK RECAPITALISATION:
Government of India announced a plan to infuse 2.11 lakh crores into public sector
banks over a period of 2 years. Of this 1.35 lakh crores will be raised via recapitalization
bonds and remaining 76,000 crores will be raised by the banks from market with budgetary
support.
BENEFITS:
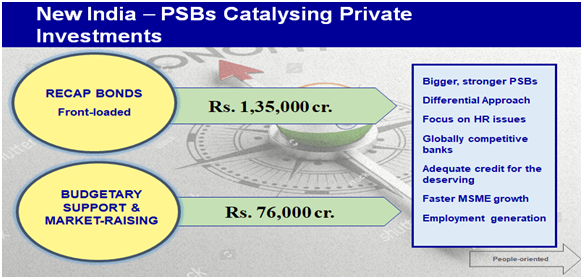 • Helps banks to compliant with Basel 3 norms • Banks will now aggressively pursue
the loan recovery • Banks with weak balance sheet problems will get relief
• Helps banks to compliant with Basel 3 norms • Banks will now aggressively pursue
the loan recovery • Banks with weak balance sheet problems will get relief
• Balances demand and supply by bringing more investments in sectors like infrastructure
• Help in efficiently managing risk and credit capital related requirements of banks
• Encourages private participation and boosts economic growth
• It will address both growth capital and capital required to absorb losses arising
out of provisioning of NPAs.
Cons :
• It will be seen as a favor to big companies and some people among small entrepreneurs
• This is only good if banks actually recognize losses otherwise it will cause extreme
inflation
• It will certainly not solve the structural problems
The Financial Resolution and Deposit Insurance Bill,2017:
• The bill seeks to create a consolidated framework for the resolution of financial
firms.
• It repeals the deposit insurance and credit guarantee corporation act, 1962 and
amends 12 other laws.
• The central government will establish a Resolution corporation.
• Risk based classification
• The bill specifies penalties for offences such as concealment of property, and
destruction or falsification of evidence.
• The service provider will automatically be liquidated if its resolution is not
completed within the maximum time period of two years.
BANKS BOARD BUREAU:
It is a part of Indradhanush plan to revamp PSBs, to improve the governance of PSBs
government constituted BBB. The bureau will recommend for selection of heads – PSBs
and Financial institutions and help banks in developing strategies and capital raising
plans. Guide banks on mergers and consolidations and also ways to address the bad
loans problems, consists of 3 ex-officio members and 3 experts in addition to chairman.
INDRADHANUSH PLAN:
• Under the Indradhanush plan action related to
1. Appointments
2. Bank board bureau
3. Capitalization
4. De-stressing PSBs
5. Empowerment
6. Framework for accountability
7. Governance reforms have been initiated by the government.
• Further under the plan the government proposed to make available 70,000 crores
out of budgetary allocations for four years to PSBs.
PANEL TO OVERSEE PSBs MERGERS:
This is called as Alternative mechanism for PSBs consolidation headed by Finance
minister, to fast-track consolidation among PSBs. This mechanism will oversee the
proposals coming from boards of PSBs for consolidation
INSOLVENCY AND BANKRUPTCY CODE:
• Insolvency and bankruptcy code (amendment)ordinance,2017 promulgated it amends
IBC, 2016.
• It aims at putting in place safeguards to prevent unscrupulous, undesirable persons
from misusing or vitiating the provisions of the code, the code provides a time-bound
process for resolving insolvency in companies and among individuals (180 days after
the process initiated, plus a 90 day extension for resolving insolvency).
Advantages:
• It will be easy for companies to exit and revival of business. • Banks and financial
institutions can easily handle the NPAs
• Create database of serial defaulters
• This will boost the economic growth
• It will remove burden from courts because adjudicating authority would be NCLT
for companies and DRT for individuals and partnership firms.
Demerits:
• It is yet to address the aspects such as lifting of moratorium in case of fraud.
• option for management of affairs by corporate debtor under supervision etc.
MERGER OF SBI ASSOCIATES WITH STATE BANK OF INDIA:
• After merger it can withstand the strong competition from private sector, and
accumulate more resources to channelize trained manpower across its branches. Cost
benefits by the way of using already existing branches instead of setting up new
branches and Economies of scale and reduction in cost of doing business.
• Visibility of the bank at global level increases
Cons:
• The associate banks have regional flavor and regional focus than the nationalistic
SBI culture
• Various internal conflicts related to pay, pension, promotion and other aspects
may arise
• After the merger , SBIs employee costs could increase by 23 crores a month.
• Negative impact would be from harmonization of accounting policies for NPA recognition
NPA ORDINANCE:
It will empower RBI to directly intervene in the bad loans resolution process; it
also conferred power upon the RBI to issue directions to banking companies for resolution
of stressed assets and allow it to specify one or more committees to advise banking
companies on resolution of stressed assets under the provisions of Insolvency and
Bankruptcy Code 2016.
BENEFITS:
• Empowering RBI will make the borrowers and bankers more responsible, the bad loan
ordinance will allow the RBI to ensure that dissenting banks come to the negotiating
table and accept resolution plans adopted by the majority of lenders or the one
that’s most feasible in the circumstances.
• They won’t be able to hold out for fear of write downs or getting caught up in
subsequent investigations by government agencies.
GYAN SANGAM:
It is an event organized to discuss the governance reforms in PSBs, the objectives
behind the meeting are ;
To take forward the governments commitments to reforms in the banking and financial
sector, to arrive at a common understanding among the professionals, regulators
and the government on the reform required in the PSBs in the current economic situations,
to provide an informal academic environment, which can bring out the creative best
of the minds of professionals and regulators.
Security Interest and Recovery of Debts Laws and Miscellaneous Provisions (amendment)act,2016:
It seeks to amend four laws:
• Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security
Interest Act,2002(SARFAESI),
• Recovery debt due to Banks and Financial Institutions Act,1993
• Indian Stamps Act,1899
• Depositories Act,1996
• The act empowers district magistrate to assist banks in taking over the management
of a company.
• The act creates a central registry to maintain records of transactions related
to secured assets.
• The act empowers RBI to examine the statements and any information of asset reconstruction
companies related to their business.
The Payments and Settlement Systems(amendment)Act,2015:
• It amends Payment and Settlement Systems Act ,2007. The act seeks to address the
problem of insolvency in the payment and settlement system by increasing transparency
and stability and bring India’s banking payment system in sync with international
practices. The amendment seeks to protect funds collected from the customers by
the payment system providers and to extend the act to cover trade repository and
legal entity identifier ,issuer.
• Issuer-it means a person who issues a legal entity identifier or similar unique
identification ,as specified by the RBI from time to time
• Legal entity identifier-it is a unique identity code assigned to a person by an
issuer to identify that person in such derivatives or financial transactions as
specified by RBI.
• It provides that an order of court, tribunal or authority which declares the system
participant as insolvent or dissolved or wound up shall not affect any settlement
that has become final and irrevocable prior to such order
INTERNAL OMBUDSMAN:
To further boost the quality of customer service and to ensure that there is undivided
attention to resolution of customer complaints in banks.
Some other initiatives:
Setting up of payment banks, white label ATMs, BHIM app, demonetization a push for
digital payments are some initiatives for promoting last mile banking services and
financial inclusion.
RBI INITIATIVES:
Strategic debt restructuring:
Under SDR, banks who have given loans to a corporate borrower get the right to convert
the full part or part of their loans into equity shares loan taken in the company.
It is initiated by the group of lenders called Joint Lending Forum (JLF)/ Debt restructuring
cell. The SDR gives banks more power in the management of the company who has taken
loan and has defaulted.
In order to achieve the change in ownership ,the JLF should collectively become
the majority shareholder by conversion of their dues from the borrower in to equity
(i.e they should collectively hold 51per cent or more of the equity shares issued
by the company and the decision to convert loan in to equity shares should be documented
and approved by the majority of the JLF members (minimum of 75per cent of creditors
by value and 60per cent of creditors by number).
Scheme for Sustainable Structuring of Stressed Assets (S4A):
The S4A scheme aims at deep financial restructuring of big debted projects by allowing
lenders (banks) to acquire equity of the stressed projects. The S4A envisages determination
of the sustainable debt level for a stressed borrower, and bifurcation of the outstanding
debt into sustainable debt and equity/quasi-equity instruments which are expected
to provide upside to the lenders when the borrowers turn around.
• Eligibility-the total loans by all institutional lender in the account should
exceed Rs 500 crore, the project should have started its commercial operations and
there should be cash flows from the project.
• The bank should hire an independent agency to evaluate how much of the debt is
sustainable.
Scheme for Sustainable Structuring of Stressed Assets (S4A):
The S4A scheme aims at deep financial restructuring of big debted projects by allowing
lenders (banks) to acquire equity of the stressed projects. The S4A envisages determination
of the sustainable debt level for a stressed borrower, and bifurcation of the outstanding
debt into sustainable debt and equity/quasi-equity instruments which are expected
to provide upside to the lenders when the borrowers turn around.
• Eligibility-the total loans by all institutional lender in the account should
exceed Rs 500 crore, the project should have started its commercial operations and
there should be cash flows from the project.
• The bank should hire an independent agency to evaluate how much of the debt is
sustainable.
CRITICISM:
Though government started with many big bang reforms in banking sector still the
sector is suffering from many problems
• The star studded Banks Board Bureau too has been unable to manage the problem,
the human resource issue at the banks remain unchanged
• The seven pronged strategy to revamp PSBs –Indradhanush is seems to be falling
apart

• Banks recapitalization will hurt governments debt-to-GDP ratio
• Ballooning NPAs in the Indian system tell us that banks and regulators have failed
to protect public money
• The problems of weak capital base are result of inefficiency and mismanagement
of the PSBs and measures like Recapitalization offers moral hazard problems and
its celebration as a decisive package makes a bad situation worse
RECOMMENDATIONS:
First, accepting P.J NAYAK committee recommendations like repeal of Bank Nationalization
Act (1970,1980),SBI act, SBI Subsidiaries Act and setting up of a Bank Investment
Company(BIC),age and tenure reforms.
Second, it is necessary to articulate in a comprehensive and transparent manner
the policy in regard to ownership and governance of both public sector and private
sector banks
Third, Banks should take serious note of the Prime Minister's statement in the Gyan
Sangam meetings to adopt latest technology and move towards paper less banking .
Fourth, the need of the hour is to understand the actual structural problems of
the banking sector and improve the governance of the Public sector banks.
Fifth, RBI measures such as Strategic Debt restructuring(SDR),joint lenders forum(JLF),and
scheme for Sustained Structuring of Stressed Assets(S4A) among others should be
implemented effectively.
Sixth, The competition from new banks and the large number of accounts opened under
the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana are two instances that could be turned in to
oppurtunities.
Seven, adapt path of economic surveys 2016 recommendation of 4Rs to address the
stressed assets (Reform, recognition, recapitalization, resolution).
Eight, economic survey 2017 suggests setting up of public sector asset rehabilitation
agency (PARA) to take charge of large bad loans in banks.
Nine, Gopal Krishna committee recommendations on recruitment, training, and staff
transfer should be accepted.
WAY FORWARD:
Banking system is the lifeline of the economic system in both developed and developing
countries. So technologically advanced, transparent, responsible, and efficient
banking sector is the need of the hour for India and in India banking is not only
about economic function of depositing and lending but it is also attached with some
social functions such as financial inclusion and inclusive growth. "The Pradhan
Mantri Mudra Loan Yojana (PMMY) is doing a great job of addressing the needs of
the youth — bank guarantee. Every youth, when they set out to do something, their
first question is "where will the money come from?". Mudra Loan Yojana has given
loans worth ₹4 lakh crore to 9.75 crore people. At this stage of socio-economic
development Consolidation, competition, and risk management are critical to the
future of banking and In order to achieve faster and inclusive economic growth,
the government, RBI, banks take a holistic relook in to the existing policies and
structures. To conclude focused attention on the new challenges may be imperative
in the largest interest of securing economic growth with equity. Once these issues
are addressed, the Indian banking sector has the potential to become further deeper
and stronger .Greater attention to these issues would facilitate finance structure
of the economy and in medium to long-term lead to broad based economic growth.
About the author:
Dr. Sasikalapushpa is Member of Parliament (Rajya Sabha) & She has also Co- authored
four books with Dr. Ramaswamy.
Dr. B. Ramaswamy is Former Pro Vice Chancellor APG
Shimla University Himachal Pradesh. He has more than 200 publications to his credit.
In his 16 years of service, Dr. Ramaswamy has served as a Bench of Magistrate, Legal
Advisor, Visiting Professor to the top Indian and International Universities besides
holding a wide range of assignments at the Govt of India.
Email: [email protected]